AP经济学知识点梳理与总结
一、 AP经济学简介
经济学是一门适用于各个专业的应用基础课程,并且是商科的专业基础课。AP经济学分为AP微观经济学和AP宏观经济学两个科目,其课程设置是按照美国大学一年级经济学公共课水平设计的,主要阐述经济学基本概念,没有复杂的数学推理,学习难度不大,是中国学生最擅长的考试科目之一。AP成绩一般大学3分及以上就可折抵学分(各学校有转换学分的具体规定)。
二、 AP宏微观经济学课程异同
AP微观经济学课程的设置是为了使学生了解经济学原理,主要是站在生产者、消费者的角度研究问题。课程涵盖了微观经济中的生产者理论、消费者理论、市场结构、以及公共物品等相关理论。课程设置中着重包括了产品市场的实质与作用,要素市场理论以及政府在促进市场有效及公平上所扮演的角色。
AP宏观经济学课程的设置目的主要是帮助学生深入了解用于研究经济体制整体的经济学原理。通过AP宏观经济学的学习,学生将彻底了解如何运用经济学原理分析一个经济体。课程设置中着重包括了国家收入、物价水平的决定因素、常用的宏观经济指标、财政政策、货币政策、经济增长理论。该课程特别注重国民收入和价格水平的确定等内容,同时,也能帮助学生更熟悉经济绩效评估指标、财政部门、稳定政策、经济增长和国际经济学等内容。
AP宏观经济学与微观经济学重合的部分主要有优势和相对优势、机会成本、边际、稀缺性、供给与需求、弹性等。如果考生同时考AP宏观和微观经济学,则重合部分一起复习即可,重合部分的出题模式在两份试卷中大体相同。
上海新航道AP课程培训中心由美国COLLEGE BOARD授权,新航道、KAPLAN教育集团共同建设,由执有AP教师培训证书的美国AP团队指导,目前我们的寒假班正在火热招生中,你还在等什么!
上海新航道2016年寒假AP课程
查看详情,请:新航道AP课程培训中心
三、 AP经济学考试结构与分数计算
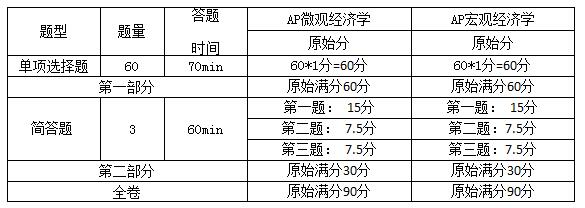
AP微观经济学以及宏观经济学均分为选择题以及简答题两个部分,考试各需要两个小时十分钟。选择题总共为60道,时间为70分钟,分数占比为2/3;简答题3道,时间为60分钟,分数占比为1/3,卷面分数为90分。
四、 2016年AP经济学考试安排
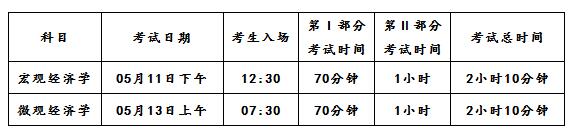
2016年AP微观经济学以及宏观经济学安排在5月13日和5月11日考试,考试时长2小时10分钟。两个科目的考试时间不冲突,考生可以同时报考两个科目。
2016年AP经济学考试时间表
五、 2016年AP经济学考试报名
报名时间报名及网上缴费时间
| 报名及网上缴费时间 | |
| AP 学校考生 | 2015年12月14日——2016年1月8日 |
| 社会考生 | 2016年1月11日——2016年1月22日 |
开考科目:详情查看请:【2016年AP考试各科时间安排表】
【新航道提供免费AP考试代报名服务,优先抢考位,如需代报名,详情查看:https://sh.xhd.cn/syjdtf/502279.html ,或者在线咨询我们的老师】
六、 AP经济学考试中的十三大要点
1 、Fundamentals of Economic Analysis
Scarce Resources
Production Possibilities
Functions of Economic Systems
2、 Demand, Supply, Market Equilibrium, and Welfare Analysis
Demand
Supply
Market Equilibrium
Welfare Analysis
3、Elasticity, Microeconomic Policy, and Consumer Theory
Elasticity
Microeconomic Policy and Applications of Elasticity
Consumer Choice
4、The Firm, Profit, and the Costs of Production
Firms, Opportunity Costs, and Profits
Production and Cost
5、Market Structures, Perfect Competition, Monopoly, and Things Between
Perfect Competition
Monopoly
Monopolistic Competition
Oligopoly
6、Factor Markets
Factor Demand
Least-Cost Hiring of Multiple Inputs
Factor Supply and Market Equilibrium
Imperfect Competition in Product and Factor Markets
7、Public Goods, Externalities, and the Role of Government
Public Goods and Spillover Benefits
Pollution and Spillover Costs
Income Distribution and Tax Structures
8、 Macroeconomic Measures of Performance
The Circular Flow Model
Accounting for Output and Income
Inflation and the Consumer Price Index
Unemployment
9、 Consumption, Saving, Investment, and the Multiplier
Consumption and Saving
Investment
The Multiplier Effect
10、Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply
Aggregate Demand
Aggregate Supply
Macroeconomic Equilibrium
The Trade-off Between Inflation and Unemployment
11、Fiscal Policy, Economic Growth, and Productivity
Expansionary and Contractionary Fiscal Policy
Difficulties of Fiscal Policy
Economic Growth and Productivity
12、Money, Banking, and Monetary Policy
Money and Financial Assets
Fractional Reserve Banking and Money Creation
Monetary Policy
13、 International Trade
Comparative Advantage and Gains from Trade
Balance of Payments
Foreign Exchange Rates
Trade Barriers