摘要:
托福TPO45听力题目+答案+MP3音频下载
Conversation 1
1. Why does the student go to see the man?(Click on 2 answers)
A To discontinue a campus service
B To pay the fee for her campus mailbox
C To get information about mailing a package
D To pick up a package
2. What does the man say about the campus mailbox service?
A Its rates for all students have recently gone down.
B It is the only way to receive certain mailings about university events
C All students are required to use it.
D It is more reliable than e-mail.
3. How does the student usually obtain information about campus events? (Click on 2 answers)
A She reads about them on the university Web site.
B She learns about them at her place of work.
C She sees the posters on a bulletin board.
D Her roommate tells her about them.
4. What does the man offer to do for the student?
A Reduce the cost of renting a mailbox
B Send her a form to fill out
C Provide university organizations with her new address
D Deliver a package to her apartment
5. Why does the student say this:
A To indicate that she agrees with the man
B To inform the man of a recent development
C To prevent a misunderstanding
D To support her own position
Conversation 2
1. Why does the woman go to see the professor?
A To get suggestions about what to include in her next presentation
B To follow up on a question she had raised in class
C To update him on a research project she is helping him organize
D To get information about a program that he had mentioned in class
2. What do the speakers agree is a benefit of the build-operate-transfer economic model that they discuss?
A It permits government engineers to work on private construction projects.
B It helps private companies buy facilities that were built by the government.
C It enables public facilities to be constructed without government funding.
D It enables private companies to operate public facilities that the government builds.
3. Why does the professor point out how much coffee is produced in Brazil?
A To give an example of the economic model the woman is interested in
B To explain why it is appropriate for him to teach a seminar about coffee
C To help clarify one of the goals of the Global Enrichment Initiative
D To correct a common misperception about Brazil's economy
4. Why is the woman interested in applying to go only to Turkey? (Click on 2 answers)
A She has been studying Turkey's history and language.
B She has already visited Brazil and Russia.
C She believes that selecting just one country will help her get accepted into the program.
D She would like to see how an economic model she studied is put into practice there.
5. What does the professor imply when he says this:
A He thinks that going first helped the woman be less nervous about giving a presentation.
B He hopes other students will structure their presentations the way the woman did.
C The woman was the first student ever to give a presentation on Turkey's economy in his class.
D He is relieved that the class is staying on schedule for making presentations
Lecture 1
1. What is the lecture mainly about?
A Reasons for the transition from religious to secular themes in Renaissance art
B The disproportionate influence of Italian artists during the Renaissance period
C Techniques used during the Renaissance to produce realistic works of art
D A comparison of themes in paintings and sculptures during the Renaissance
2. What is the professor's opinion of Leon Battista Alberti as an artist?
A Alberti’s interests were too diverse for him to succeed in any one field
B Alberti was ineffective in imposing his own theories on other artists.
C Alberti was a much more skilled artist than da Vinci or Michelangelo.
D Alberti represents the Renaissance ideal of wide-ranging achievement.
3. According to the professor, what did Alberti consider to be the most important aspect of a Renaissance painting?
A That it convey an appealing narrative
B That its figures be posed symmetrically
C That its theme not be religious
D That its characters be positioned within a landscape
4. Why did some artists begin to use the contrapposto pose?
A To create a cartoon-like effect
B To help viewers identify the main figure in a work of art
C To show the relative sizes of human figures
D To make human figures appear more natural
5. Why does the professor discuss tendons and muscles?
A To emphasize that Alberti’s study of anatomy led to his interest in art
B To show the emphasis Alberti placed on using physically fit models
C To illustrate the difficulty of maintaining a contrapposto pose in real life
D To explain one of Alberti's methods for creating accurate proportions
6. Why was the development of linear one-point perspective important to Renaissance artists?
A It helped painters to place figures more symmetrically within their paintings.
B It allowed painters to create an illusion of three dimensions.
C It enabled artists to paint large landscapes for the first time.
D It encouraged artists to take an interest in geometry.
Lecture 2
1. What is the lecture mainly about?
A The process by which immune cells are produced
B The effects of consuming far fewer calories than usual
C The function of an organ found in rhesus monkeys and in humans
D The discovery of a nutrient necessary for good health
2. Why does the professor mention the thymus?
A To explain how different types of food are turned into energy
B To give an example of an organ attacked by certain bacteria
C To introduce a research study by a nutritional biologist
D To answer a question about certain immune cells
3. According to the professor, why are some cells called "naive"?
A They originate from a relatively primitive type of cell.
B They are easily eliminated by the immune system.
C They are not yet able to recognize any particular protein marker.
D They can become part of any one of various organs of the body.
4. In a recent study mentioned by the professor, what are two differences between the monkeys that have been fed a normal diet and the ones that have not?(Click on 2 answers)
A The monkeys on a normal diet appear older.
B The monkeys on a normal diet get sick less often.
C The monkeys on a normal diet have fewer naive T cells.
D The monkeys on a normal diet tend to live longer.
5. What does the professor think about a calorie-restricted diet?(Click on 2 answers)
A She would not find it easy to follow.
B She is not sure humans would benefit from it
C Doctors are not likely ever to recommend it for people.
D It would probably affect humans differently than it affects monkeys.
6. What does the professor mean when she says this:
A Problems in the study make its conclusions difficult to believe.
B The actual effect on mice was not what it seemed.
C Other studies of mice produced different results.
D Other animals seem to react as mice do.
Lecture 3
1. What does the professor mainly discuss?
A Characteristics of different types of mixtures
B Differences between mixtures and solutions
C Ways of separating components of mixtures
D Identifying variable properties of solutions
2. In the lecture, the professor gives examples of homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures. For each mixture below, indicate which kind it is.
Click in the correct boxes
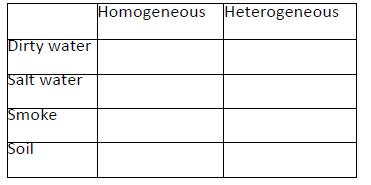
3. What is one basis for classifying a mixture as homogeneous or heterogeneous?
A Whether its component parts are the same type of matter
B Whether its component parts are present in equal proportions
C Whether it contains one phase or more than one phase
D Whether it appears, without magnification, to contain a single component
4. What can be inferred from the lecture about the process of distillation?
A It cannot be used if a mixture has variable properties.
B It can be used to separate the components of homogeneous mixtures.
C It is used to change heterogeneous mixtures Into homogeneous mixtures.
D It is a more efficient way of separating components of heterogeneous mixtures than filtration.
5. Why does the professor mention the freezing point of a mixture?
A To explain why salt dissolves in water
B To emphasize that mixtures can exist in a frozen state
C To show how filtration and distillation differ
D To give an example of a variable property of mixtures
6. What does the professor imply when he says this:
A He wants to correct a statement he made previously.
B He is uncertain whether the students understood his explanation.
C The meaning of a term should be obvious to the students.
D The students are probably unaware that they have already seen examples of heterogeneous mixtures.
Lecture 4
1. What is the main purpose of the lecture?
A To explore possible solutions to an anthropological mystery
B To analyze the results of a nutritional experiment
C To explain why human beings first started creating ceramics
D To examine changes in the dietary preferences of an ancient culture
2. According to the professor, wtiy would the ceramic vessels used by ancient Arctic people be likely to break?
A Ancient Arctic people used cooking techniques unsuitable for ceramic pots.
B Ancient Arctic people were frequently moving from place to place.
C The vessels were not made with high-quality clay.
D The vessels were often exposed to extreme temperatures.
3. Why does the professor mention that the Arctic climate is cold and wet?
A To explain why ancient Arctic people found warm food appealing
B To explain why ancient Arctic people required a diet that was rich in meat
C To explain the difficulties of manufacturing pottery in such a climate
D To explain why some foods could not be stored in clay pots
4. What does the professor imply about ancient Arctic people’s food preferences?
A They liked raw foods better than minimaIly cooked foods.
B They enjoyed eating foods that had been prepared in contrasting ways.
C Their preferences changed dramatically over time.
D They liked foods cooked in ceramic vessels better than foods cooked in other types of containers.
5. According to the professor, why did ancient Arctic people cook using small fires?(Click on 2 answers)
A Their pottery could not withstand intense heat.
B Small fires made it easier to control cooking speed.
C Cooking had to be done indoors.
D Fuel was difficult to obtain.
6. Why does the student say this:
A He wants to make sure the professor is referring to the past and not the present.
B He does not understand why making ceramics in the Arctic is considered challenging.
C He thinks the fact that ancient Arctic people made ceramics requires some explanation.
D He does not believe the ancient Arctic people actually made ceramics.
托福TPO45听力答案
CONVERSATION1:1.AC 2.B 3.BC 4-5.AC
CONVERSATION2:1-3.DCB 4.AD 5.D
LECTURE1:1-6.CDADDB
LECTURE2:1-3.ADC 4.AC 5.AB 6.D
LECTURE3:1.A 2BABB 3-6.CBDC
LECTURE4:1-4.ABCB 5.CD 6.C
上海新航道整理!由于音频文件不便上传,想要托福TPO45听力题目+答案+MP3音频下载的同学,请提交“姓名+电话+邮箱”,我们将于15个小时内发送给您!
更多托福TPO听力原文+MP3音频查看及下载,请移步:https://sh.xhd.cn/toefl/tpotingli/
免费领取最新剑桥雅思、TPO、SAT真题、百人留学备考群,名师答疑,助教监督,分享最新资讯,领取独家资料。
方法1:扫码添加新航道老师

微信号:shnc_2018
方法2:留下表单信息,老师会及时与您联系
| 课程名称 | 班级人数 | 课时 | 学费 | 报名 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 托福入门段(A段)6-10人走读班 | 6-10人 | 80课时 | ¥15800 | 在线咨询 |
| 托福强化段(C段)6-10人班 | 6-10人 | 96课时 | ¥30800 | 在线咨询 |
| 托福全程段(A+B+C段)6-10人班 | 6-10人 | 224课时 | ¥55800 | 在线咨询 |
| 托福特训班(4周,走读) | 8-10人 | 192 | ¥34800 | 在线咨询 |
| 托福特训班(6周,走读) | 8-10人 | 288 | ¥49800 | 在线咨询 |
| 课程名称 | 班级人数 | 课时 | 学费 | 报名 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 托福精讲段(B段)20-30人班 | 20-30人 | 96课时 | ¥7800 | 在线咨询 |
| 托福强化段(C段)20-30人班 | 20-30人 | 96课时 | ¥8800 | 在线咨询 |
| 托福全程段(A+B+C段)20-30人班 | 20-30人 | 192课时 | ¥13800 | 在线咨询 |
| 课程名称 | 班级人数 | 课时 | 学费 | 报名 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 托福入门段(A段)(6-10人,住宿) | 6-10人 | 80课时 | ¥17800 | 在线咨询 |
| 托福强化段(C段)6-10人班住宿 | 152课时 | ¥33800 | 在线咨询 | |
| 托福全程班(A+B+C段)6-10人班住宿 | 6-10人 | 304课时 | ¥60800 | 在线咨询 |
| 托福长线班(6-10人,住宿) | 6-10人 | 272课时 | ¥77800 | 在线咨询 |
| 托福词汇语法住宿班(A段)(6-10人) | 6-10人 | 48课时 | ¥8800 | 在线咨询 |
| 课程名称 | 班级人数 | 课时 | 学费 | 报名 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 托福全程段(A+B+C段)20-30人班住宿 | 20-30人 | 192课时 | ¥15800 | 在线咨询 |
| 托福强化段(C段)20-30人班住宿 | 20-30人 | 96课时 | ¥8800 | 在线咨询 |
| 托福精讲段(B段)20-30人班住宿 | 20-30人 | 96课时 | ¥9800 | 在线咨询 |
| 课程名称 | 班级人数 | 课时 | 学费 | 报名 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 托福一对一 | 1 | 按需定制 | ¥980元 | 在线咨询 |
| 托福免费试听课 | ¥0元 | 在线咨询 |
| 课程名称 | 班级人数 | 课时 | 学费 | 报名 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 小托福考试技巧进阶课程 | 30 | ¥9800 | 在线咨询 |
免责声明
1、如转载本网原创文章,请表明出处;
2、本网转载媒体稿件旨在传播更多有益信息,并不代表同意该观点,本网不承担稿件侵权行为的连带责任;
3、如本网转载稿、资料分享涉及版权等问题,请作者见稿后速与新航道联系(电话:021-64380066),我们会第一时间删除。
地址:徐汇区文定路209号宝地文定商务中心1楼
乘车路线:地铁1/4号线上海体育馆、3/9号线宜山路站、11号线上海游泳馆站
总部地址:北京市海淀区中关村大街28-1号6层601 集团客服电话:400-097-9266 总部:北京新航道教育文化发展有限责任公司
Copyright © www.xhd.cn All Rights Reserved 京ICP备05069206

 微信公众号
微信公众号
 微信社群
微信社群